基本类型包装类
Java 并不是纯面向对象的语言,虽然java语言是一个面向对象的语言,但是Java的基本数据类型并不是面向对象的。Java中的基本类型,如果想通过对象的形式去使用他们,Java提供的基本类型包装类,使得Java能够更好的体现面向对象的思想,同时也使得基本类型能够支持对象操作!
包装类介绍
一下是包装类的层次结构,下面表示的是一个继承类
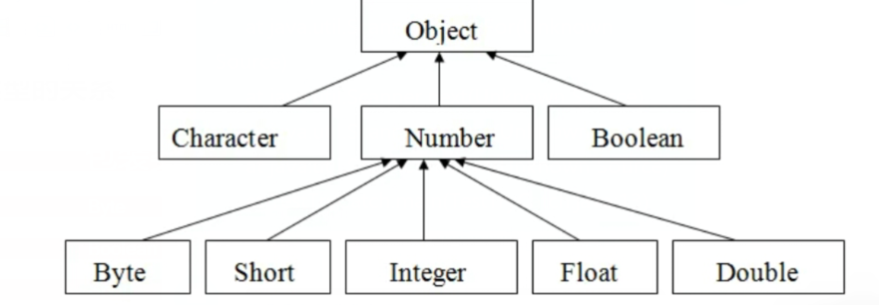
想Byte、Short、Integer等等这些就是继承自Number类,而他们都是继承至Object
下面使用Integer来作为示例,这里将10这个int类型封装成为了一个类
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i = new Integer(10);
}
}
Integer文件中是可以看到它是如何封装的
private final int value; //这个就是传入的基本类型,final表示不能修改
/**
* Constructs a newly allocated {@code Integer} object that
* represents the specified {@code int} value.
*
* @param value the value to be represented by the
* {@code Integer} object.
*/
public Integer(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
在我的理解就类似于,我一下编写的类
package com.company.zy01;
public class IntTest {
public final int value; //这里就是将int值传入封装成一个类
public IntTest(int value){
this.value=value;
}
}
```java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IntTest j = new IntTest(10);
}
}
但是不同于上面我自己编写的简简单单的类,包装类功能强大的多:
:star: 包装类支持自动装箱(直接将对应的基本类型传入),还可以自动拆箱
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i = 10; //直接作为int类型使用,不需要创建对象
}
}
这里其实是使用了一个valueof来传递
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i = Integer.valueOf(10); //和什么作用一样
}
}
可以点进去看看这个文件,
返回表示指定int值的Integer实例。如果不需要新的Integer实例,通常应该优先使用构造函数Integer(int),因为该方法通过缓存频繁请求的值,可能会显著提高空间和时间性能。这个方法总是缓存-128 ~ 127(包括-128 ~ 127)范围内的值,也可能缓存范围以外的值。也就是说Integer包装类会在缓存中自动创建这个范围了的值
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
//首先判断是不是-128~127以内的值
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
//如果是就直接访问缓存的值
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
//如果不是,则创建一个新对象
return new Integer(i);
}
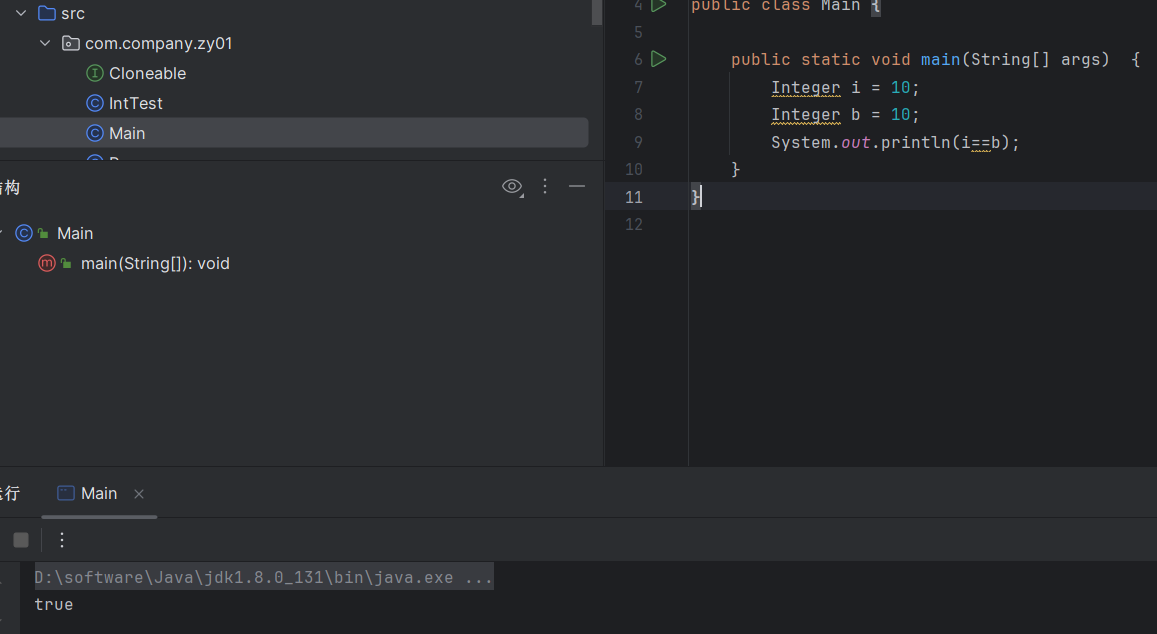
可以试一下,可以看到虽然他们变量名不一样,但是由于数据是缓存范围内的,所以说他们指向的都是同一个对象
这里它就是不同类型,因为在这个数值范围不在缓存内
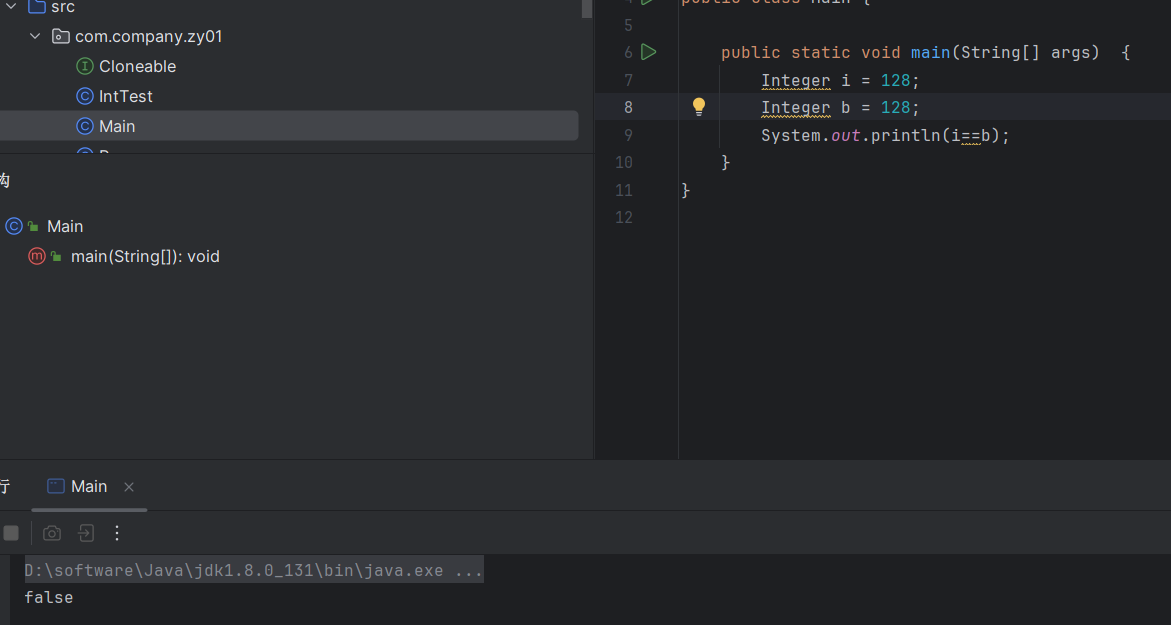
而且如果使用包装类创建两个不同的对象,肯定也是不一样的
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i = new Integer(10);
Integer b = new Integer(10);
}
}
包装类的拆箱,可以直接赋予给基本类型
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i = new Integer(10);
int a = i;
}
}
:star: 前面提到了包装类要比普通类强大,就是因为它提供了很多方法
字符串转换,直接传入
字符串public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer i = new Integer("666"); System.out.println(i); } } //也可以使用valueof public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer i = Integer.valueOf("666"); System.out.println(i); } }进制转换
//十六进制 public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer i = Integer.decode("0x1f"); System.out.println(i); } } //十进制 public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(166)); } }包装类常量
MAX_VALUE,MIN_VALUE这两个常量可以查看最大值和最小值
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("int的最大值:" + Integer.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println("int的最小值:" + Integer.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("byte的最大值:" + Byte.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println("byte的最小值:" + Byte.MIN_VALUE);
}
}
等等还有很多可以参考这篇博客Java 八大包装类(超详细!)_八种基本数据类型的包装类-CSDN博客
特殊包装类
除了我们上面人数的这几个包装类型之外,还有几个比较特殊的包装类型
第一个就是用于计算超大数组的BigInteger,它可以计算比long还要长的数据
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigInteger i = BigInteger.valueOf(Long.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println(i);
}
}

:warning: 注意BigInteger不能和int、long等类型直接进行运算,而且不能使用常用的运算符来进行计算
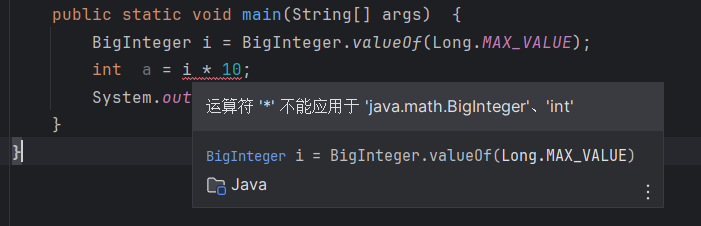
:star:但是类里面由很多运算操作比如multiply计算乘法
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigInteger i = BigInteger.valueOf(Long.MAX_VALUE);
BigInteger a = i.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(10)); //必须两个都是BigInteger类型的
System.out.println(a);
}
}
:star: 使用pow计算乘方
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigInteger i = BigInteger.valueOf(Long.MAX_VALUE);
i = i.pow(100);
System.out.println(i);
}
}

接下来再来看BigDecimal它可以计算精确计算的场景,可以实现小数的精确计算
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal i = new BigDecimal(10);
//100表示精确到小数点100位,RoundingMode.CEILING表示舍入模式,CEILING表示向下取整.FLOOR表示向上取整
i = i.divide(BigDecimal.valueOf(3),100, RoundingMode.FLOOR);
System.out.println(i);
}
}


